Prompt Engineering in AI? What the * is That?
Prompt engineering in AI isn't just jargon—it's the key to getting the right results. Learn how to optimize your interactions with AI through clear prompts and avoid AI hallucinations, from Google and Gemini strategies. Happy engineering, fellow Prompt Engineers!

Ah, "prompt engineering"—the latest party trick for anyone dabbling with AI who wants to sound sophisticated.
But beyond the buzzwords and the mystique, what the heck is prompt engineering?
Well, the meaning of prompt engineering is – the way we're just talking to computers or sort of ????
Believe it or not, the way you talk to your AI—whether you're asking it to write a story, craft an email, or create a masterpiece—makes a massive difference in what you get back.
While building my AI tools, I struggled with how to ensure that the AI returned the best possible output based on the user's input.
I've read a lot of articles (I'm sharing some of them in this article) and finally improved my prompts templates.
And based on these surveys, it seems I've done it right ????
This article aims to quickly introduce you to prompt engineering, and shortly explain a few new fancy words, such as zero-shot and few-shot prompts and AI Hallucinations.
Also, you'll find the basic best practices to get started with prompt engineering as a beginner.
Let's start with a few articles I want to mention!
The first article I want to mention comes from the Google Developers blog, which is about the basics of prompt engineering.
One thing that helped me a lot from this article is this prompt example:
Prompt: You are a mighty and powerful prompt-generating robot. You need to understand my goals and objectives and then design a prompt. The prompt should include all the relevant information context and data that was provided to you. You must continue asking questions until you are confident that you can produce the best prompt for the best outcome. Your final prompt must be optimized for chat interactions. Start by asking me to describe my goal, then continue with follow-up questions to design the best prompt.
I was able to create my prompts templates using ChatGPT and this prompt (with some minor changes), but in the end, I had what I needed.
ChatGPT kept asking me questions until it sent me the best prompt template.
The second article I want to mention comes from Gemini prompts strategies (also a Google blog), which are applied to all Generative AIs, not only Gemini.
This article made me clear what zero-shot and few-shot prompts are.
What are 'Zero-shot vs few-shot prompts'?
In prompts, you can show the model how to do things right by giving examples. The model looks at these examples to understand how to make its responses.
If a prompt has a few examples, it's called a few-shot prompt. If it has no examples, it's called a zero-shot prompt. Zero-shot vs few-shot prompts (source https://ai.google.dev/gemini-api/docs/prompting-strategies)
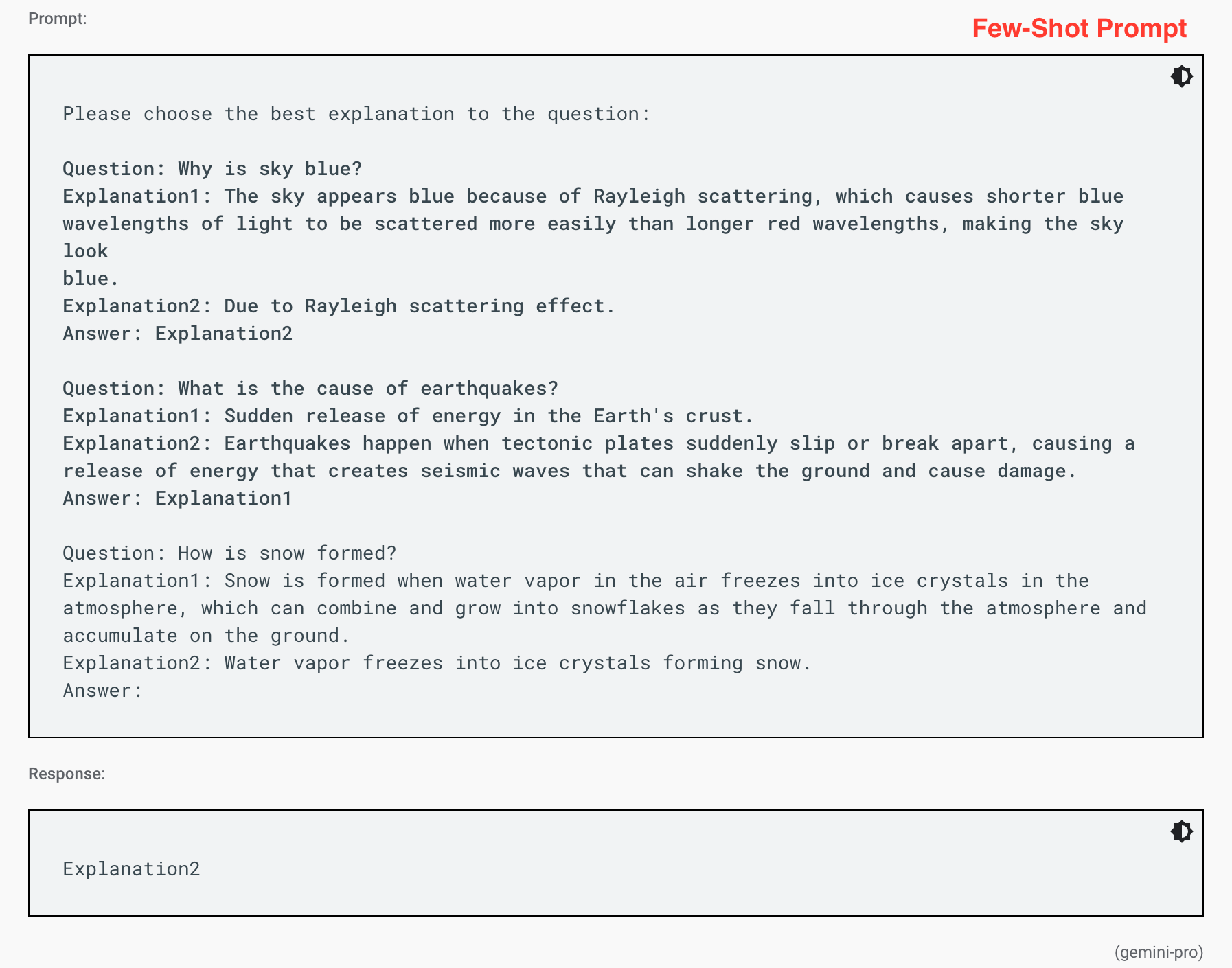
Few-shot prompts help the model understand how to structure its responses better. It's good to use specific and different examples to help the model focus and give better answers.
It's suggested to always include examples in your prompts. If your examples are clear enough, you might not even need to give instructions in your prompt.
If you want to learn more about prompting strategies, check the images' source link, it has plenty of them.
3 Best Practices for Prompt Engineering (for Beginners)
In the world of AI, where machines attempt to understand and respond to human language, prompt engineering plays a crucial role in guiding these interactions.
Here are the three best practices I found out for beginners, to achieve better outcomes. It's worth mentioning that there are more in-depth techniques and strategies, you can read about here, here, and here ????.
But for beginners, here's what I advise ⤵️
1. Keep it Clear and Precise
Imagine explaining a task to a friend—you wouldn't want to leave them guessing about what you're asking for.
Similarly, AI models need clear guidance to provide accurate responses. Using specific language and avoiding ambiguity can help ensure that the model understands exactly what you're requesting.
For example, instead of prompting - "Tell me about dogs.", you can say - "Provide a brief description of the Golden Retriever breed, including their temperament and ideal living environment" Lacks clarity vs more specific prompts

2. Adopt a persona (Act as ..., You are ...)
Another effective technique in prompt engineering is to adopt a persona when communicating with AI models.
By imagining who you're talking to—a helpful assistant, an expert, or even a friendly pet—you can tailor your prompts to match the intended tone and style. 

This not only helps the model understand the context of your request but also adds a human touch to the interaction, making it more engaging and relatable.
3. Specify the format
Lastly, when designing prompts, it's essential to specify the desired format for the response.
Whether you're asking for a paragraph of text, a list of bullet points, or a creative story, providing clear instructions on the expected format helps the AI model generate more relevant and useful outputs. No desired format vs desired format prompt

This ensures that the response aligns with your needs and preferences, minimizing the risk of misinterpretation or errors.
All these tips sound fun and easy, but you should remember that there's no simple ONE ideal strategy that works for each task; you should always try different strategies until AI gives you the right output.
Sometimes (or more often), you might get an answer that is not quite right, or even more - wrong. This is what is called AI Hallucinations!
What are AI Hallucinations?
AI hallucinations refer to instances when an AI model produces incorrect information but presents it as factual.
In simpler terms, imagine asking your AI for information, and instead of getting a helpful response, you receive a bunch of nonsense that the AI thinks you want to hear.
It's like your AI buddy getting a bit too excited and making things up as it goes along, without considering whether what it's saying makes sense.
AI hallucinations highlight the need for caution and critical thinking when interpreting the outputs of AI models, as they may not always provide reliable or accurate information.
To prevent AI Hallucinations, IBM has a great post about this.
Conclusion
So there you have it — prompt engineering isn't just about bossing around your AI, it's an art form, a science, and, yes, maybe even a bit of engineering.
With clear and precise instructions, a well-defined persona, and specified formatting requirements, you can ensure that the AI understands your requests accurately and delivers responses that meet your expectations.
So, the next time you're stuck with a mediocre AI output, remember that maybe it's not the AI. Perhaps it's your prompt. ????????♂️
Happy engineering, fellow Prompt Engineers! Keep those prompts crisp, and may your outputs always be brilliant.