Copycat Apps: The impact on Innovation, AI Saturation, and Prompts
Explore how copycat apps from mobile games to AI tools impact innovation, and economics - while prompts are never going to go away as a result.

Introduction

The mobile app market has seen explosive growth in recent years, with millions of apps now available across various platforms. This surge in availability, however, has also led to an increase in the number of copycat apps—imitations of popular apps that seek to capitalize on the success of the originals. Take, for example, the wildly popular Flappy Bird game, which spawned a slew of imitators like Flappy Bat and Flappy Cow, each attempting to ride the coattails of the original's success. These copycat apps are often created with minimal effort and at low cost, offering developers a quick entry into the market. But what does this mean for innovation in the AI tech industry?
Copycat apps occupy a controversial space in the tech world. On one hand, they can stifle innovation by discouraging original developers from investing in new ideas when they know their work might be swiftly copied. On the other hand, the pressure from these imitators can push developers to innovate further, refining their products to stay ahead of the competition. This dual role of copycat apps—both as a potential threat to creativity and a catalyst for innovation—makes them a fascinating phenomenon worthy of deeper exploration.
This article will go into the evolution of copycat apps, starting from their early days in the mobile gaming space and tracing their journey into the realm of artificial intelligence (AI). As we explore this trend, we'll examine how the proliferation of AI-powered tools, many of which are built on similar underlying technologies, has cemented the importance of prompts in driving AI interactions. By the end of this piece, it will become clear that the ongoing reliance on prompts is not just a temporary phase but a critical component of the AI landscape, driven in large part by the very nature of copycat innovation.
The Proliferation of Copycats
Copycat apps are, by definition, applications that closely replicate or imitate the design, functionality, or concept of an original, successful app (Wang, Li, & Singh, 2018). These apps often emerge in the wake of a popular app’s success, offering slight variations or rebranding while largely maintaining the core features that made the original app popular. This practice became especially prevalent during the mobile gaming boom, with "Flappy Bird" serving as a prime example. The success of "Flappy Bird" led to a wave of imitators like "Flappy Bat" and "Flappy Cow," all of which tried to capture the same audience with minimal changes to the original gameplay. The low cost of entry and the availability of development tools have made it easy for developers to create these imitations quickly, leading to a crowded app marketplace where originality can be hard to discern.
The Economic Appeal
The economic incentives behind creating copycat apps are significant, especially when considering the lower risk and investment required compared to developing an original app (Sigg, Lagerspetz, Peltonen, Nurmi, & Tarkoma, 2019). For developers, the appeal lies in the ability to capitalize on an existing user base without the need for extensive research, development, or marketing efforts. The quick time to market means that copycat apps can be launched rapidly, often while the original app is still riding its wave of popularity. This approach allows developers to tap into the same audience that propelled the original app to success, often resulting in quick returns with minimal financial risk. The financial dynamics in play can sometimes lead to situations where copycat apps outperform their original counterparts, particularly when they are able to provide a similar user experience at a lower cost or with additional features.
The proliferation of copycat apps has a complex relationship with innovation in the tech industry (Li, Singh, & Wang, 2014). On one hand, the saturation of the market with near-identical apps can stifle creativity, as original developers may become discouraged from investing time and resources into new projects, knowing that their work could be easily replicated. This could lead to a homogenization of the app ecosystem, where originality is sacrificed for the sake of quick profits. However, it’s also true that the presence of copycats can serve as a catalyst for further innovation. Original developers, in response to the threat posed by imitators, may be driven to continuously improve their products, adding new features, enhancing user experience, and finding ways to differentiate themselves from the competition. Additionally, some copycat apps inadvertently boost the visibility of the original app by drawing more attention to the genre or category it belongs to, creating a spillover effect that can benefit the original creators.
Copycats with AI Tools
The copycat phenomenon has not been limited to mobile apps alone. With the rise of AI tools, particularly those powered by OpenAI’s API, a new frontier for copycat development has emerged. Developers are leveraging existing AI models to create their own versions of popular tools, often adding slight modifications or rebranding them to appeal to different market segments. For example, PdfGPT charges $20 a month for a feature that can be replicated with the right prompts in ChatGPT, which is significantly more affordable. Similarly, CopyAI, at $36 a month, and Jasper, at $49 a month, offer services that essentially use the same underlying technology as ChatGPT, yet with a premium price tag. This trend reflects a broader shift where the cost of developing original AI has made repurposing existing models an attractive option for many developers. As a result, the AI space is becoming increasingly saturated with tools that, while technically different, offer very similar functionalities (Hopp, 2024).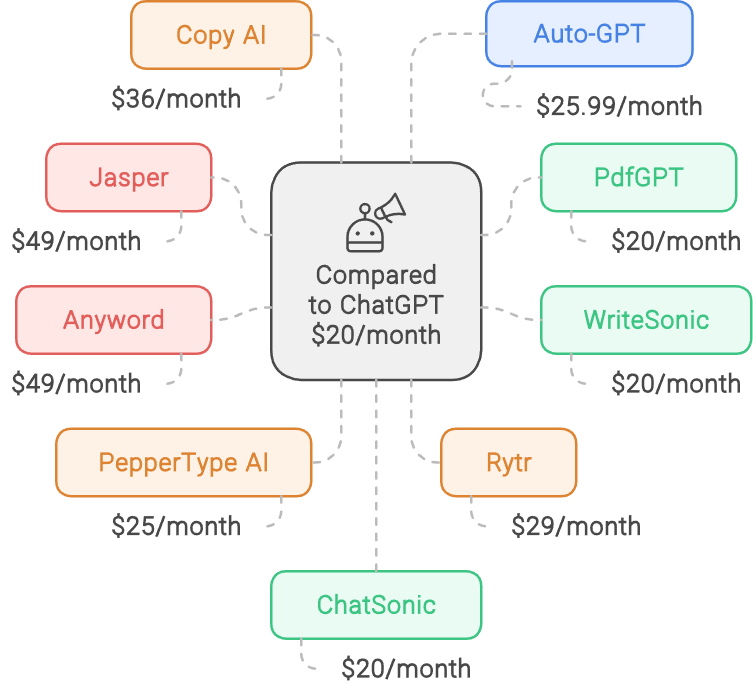
The challenges and costs associated with developing original AI models are substantial. Creating a new AI tool from scratch requires significant financial resources, technical expertise, and time. This reality has driven many developers to rely on existing infrastructures like OpenAI’s API, which provides a robust foundation upon which to build customized applications. By utilizing these pre-existing models, developers can focus on adding specific features or targeting niche markets, rather than investing in the complex process of developing an AI from the ground up. This economic model has led to a proliferation of AI tools that, while branded as unique, often share much of their core functionality with other tools on the market. The reliance on established AI frameworks has thus become a key factor in the growth of copycat apps in the AI space (Wen & Zhu, 2016).
To understand the impact of copycat AI tools on the market, it’s helpful to compare specific examples. PdfGPT, for instance, charges users $20 a month to use GPT-4 for interacting with PDFs—a feature that can be achieved with ChatGPT using the right prompt at a much lower cost. Similarly, CopyAI and Jasper offer content creation tools at $36 and $49 a month, respectively, yet both are built on the same underlying technology as ChatGPT. The key difference lies in how these tools are marketed and the additional features they claim to provide. However, for users who are proficient in crafting prompts, ChatGPT can perform many of the same tasks at a fraction of the cost. These case studies illustrate how copycat AI tools often capitalize on the convenience of pre-packaged solutions, despite offering little in terms of truly novel functionality. This raises questions about the value proposition of these tools and the extent to which they rely on user perceptions rather than actual technological advancements (Gregori, 2017; Hopp, 2024).
Moving Past using Prompts?
Prompts have become an essential element in the use of AI tools, particularly as the market becomes saturated with applications that are fundamentally similar in their underlying technology. The effectiveness of an AI tool often hinges on the quality of the prompts provided by the user, which can significantly influence the output. This is especially true in a landscape filled with copycat apps that, while offering different interfaces or slight feature variations, ultimately rely on the same AI engines. In such an environment, the ability to craft precise and creative prompts can be the difference between a mediocre and an exceptional user experience. For instance, while PdfGPT, CopyAI, and Jasper package specific functionalities with a higher price tag, users who master prompt engineering can achieve comparable results with ChatGPT at a fraction of the cost. This reliance on prompts underscores their ongoing importance as a critical skill in the AI era (Jain & Jain, 2023).
Why Prompts are Here to Stay
Given the current landscape of AI development, where many tools share similar foundations, the importance of prompts is unlikely to diminish anytime soon. As more developers create tools based on pre-existing AI models, the value of knowing how to effectively interact with these models through prompts will continue to grow. The saturation of AI tools has made it clear that innovation in user experience is often less about the underlying technology and more about how that technology is leveraged through user input. This means that, as long as AI tools are built on comparable infrastructures, the skill of prompt engineering will remain essential. Moreover, as AI continues to evolve, prompts may become even more sophisticated, requiring users to continually refine their approach to interacting with these systems. This trend suggests that learning and mastering prompts is not just a temporary necessity but a long-term skill that will be crucial for navigating the AI landscape (Hopp, 2024).
Looking ahead, the role of prompts in AI interactions is likely to evolve as technology advances. While it's possible that future AI developments could lead to more intuitive interfaces that reduce the reliance on user-generated prompts, the fundamental need for clear and effective communication with AI systems is unlikely to disappear. As AI tools become more complex, the prompts themselves may need to become more nuanced, allowing users to fine-tune outputs in increasingly sophisticated ways. Additionally, as AI becomes more integrated into various aspects of daily life, the ability to craft effective prompts could become a valuable skill across multiple domains, from business to education to personal use. Despite the potential for more advanced AI interfaces, the current trajectory suggests that prompts will continue to play a central role in how we interact with AI, making prompt engineering an indispensable skill for the foreseeable future (Jain & Jain, 2023).
Recap of Key Points
Throughout this article, we've explored the intricate dynamics of the copycat phenomenon across different tech landscapes, from mobile apps to AI tools. We began by examining how copycat apps have emerged as both a challenge and a driver of innovation, particularly in the mobile gaming sector with examples like Flappy Bird. We then transitioned to the AI realm, where the rise of tools like PdfGPT, CopyAI, and Jasper illustrates how developers are capitalizing on existing AI models to create slightly modified, yet higher-priced versions of tools that essentially perform the same functions as ChatGPT. This discussion highlighted the economic incentives behind copycat development and its impact on the tech industry. Finally, we delved into the critical role of prompts in this saturated market, emphasizing that mastering prompt engineering is not just a skill for today but an essential tool for the future of AI interactions.
The copycat phenomenon, while often seen as a negative force in tech development, also presents opportunities for both innovation and user empowerment. As developers continue to repurpose existing technologies, the importance of creativity in how these tools are used becomes even more pronounced. For users, this means that learning to effectively interact with AI through prompts can unlock the full potential of these tools, often at a fraction of the cost offered by more expensive alternatives. As we look to the future, the landscape of AI is likely to become even more competitive, with both challenges and opportunities for those who are willing to innovate not just in technology but in how they engage with it. The ongoing evolution of AI tools underscores the importance of staying ahead of the curve, and for now, that means mastering the art of prompt engineering.
Sources
- Hopp, D. (2024). Free to play: UN Trade and Development's experience with developing its own open-source Retrieval Augmented Generation Large Language Model application. arXiv. Retrieved from https://arxiv.org/abs/2407.16896
- Wen, W., & Zhu, F. (2016). Threat of Platform-Owner Entry and Complementor Responses: Evidence from the Mobile App Market. Sources of Innovation eJournal. Retrieved from https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/932a4fd9013de4d12b6d415e25b96f4d4fa8b03b
- Gregori, E. (2017). Evaluation of Modern Tools for an OMSCS Advisor Chatbot. Retrieved from https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/31e930e792c5055633501721380aa4bbbcc71fe6
- Jain, R., & Jain, A. (2023). Generative AI in writing research papers: A new type of algorithmic bias and uncertainty in scholarly work. arXiv. Retrieved from https://arxiv.org/abs/2312.10057
- Wang, Q., Li, B., & Singh, P.V. (2018). Copycats vs. Original Mobile Apps: A Machine Learning Copycat-Detection Method and Empirical Analysis. Inf. Syst. Res., 29, 273-291. Retrieved from https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/36c286fb130216fa8e0fcfe46e2cb6cd18d2b25e
- Sigg, S., Lagerspetz, E., Peltonen, E., Nurmi, P., & Tarkoma, S. (2019). Exploiting Usage to Predict Instantaneous App Popularity. ACM Transactions on the Web (TWEB), 13, 1 - 25. Retrieved from https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/ba157d700d7a3299ad58a71c017528f22ee9474d
- Li, B., Singh, P.V., & Wang, Q. (2014). Zoom in iOS Clones: Examining the Impact of Copycat Apps on Original App Downloads. Retrieved from https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/3a817c26885f72c7cbb15b1ca1c0cacbfffd08b1